numpy.hanning#
- numpy.hanning(M)[source]#
返回汉宁窗。
汉宁窗是一种通过加权余弦形成的锥形窗。
- 参数:
- Mint
输出窗中的点数。如果为零或负数,则返回空数组。
- 返回:
- outndarray, shape(M,)
窗,其最大值归一化为一(值“一”仅在 M 为奇数时出现)。
注释
汉宁窗定义为
\[w(n) = 0.5 - 0.5\cos\left(\frac{2\pi{n}}{M-1}\right) \qquad 0 \leq n \leq M-1\]汉宁窗以奥地利气象学家 Julius von Hann 的名字命名。它也被称为余弦钟。一些作者更倾向于称其为 Hann 窗,以避免与非常相似的 Hamming 窗混淆。
大多数关于汉宁窗的引用都来自信号处理文献,其中它被用作众多窗函数之一,用于平滑值。它也称为“切趾”函数(意为“去除足部”,即平滑采样信号开头和结尾的不连续性)或锥形函数。
参考文献
[1]Blackman, R.B. and Tukey, J.W., (1958) The measurement of power spectra, Dover Publications, New York.
[2]E.R. Kanasewich, “Time Sequence Analysis in Geophysics”, The University of Alberta Press, 1975, pp. 106-108.
[3][4]W.H. Press, B.P. Flannery, S.A. Teukolsky, and W.T. Vetterling, “Numerical Recipes”, Cambridge University Press, 1986, page 425.
示例
>>> import numpy as np >>> np.hanning(12) array([0. , 0.07937323, 0.29229249, 0.57115742, 0.82743037, 0.97974649, 0.97974649, 0.82743037, 0.57115742, 0.29229249, 0.07937323, 0. ])
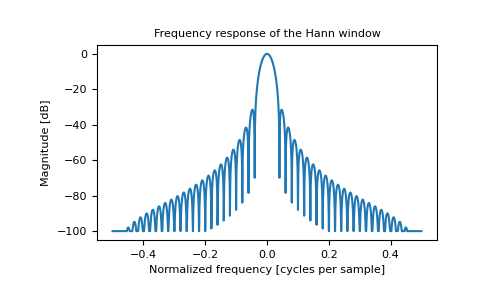
绘制窗及其频率响应。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from numpy.fft import fft, fftshift window = np.hanning(51) plt.plot(window) plt.title("Hann window") plt.ylabel("Amplitude") plt.xlabel("Sample") plt.show()
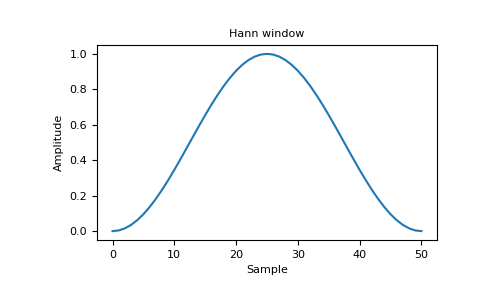
plt.figure() A = fft(window, 2048) / 25.5 mag = np.abs(fftshift(A)) freq = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, len(A)) with np.errstate(divide='ignore', invalid='ignore'): response = 20 * np.log10(mag) response = np.clip(response, -100, 100) plt.plot(freq, response) plt.title("Frequency response of the Hann window") plt.ylabel("Magnitude [dB]") plt.xlabel("Normalized frequency [cycles per sample]") plt.axis('tight') plt.show()