numpy.histogram2d#
- numpy.histogram2d(x, y, bins=10, range=None, density=None, weights=None)[source]#
计算两个数据样本的二维直方图。
- 参数:
- x类数组, 形状 (N,)
一个数组,包含要进行直方图处理的点的 x 坐标。
- y类数组, 形状 (N,)
一个数组,包含要进行直方图处理的点的 y 坐标。
- bins整数 或 类数组 或 [整数, 整数] 或 [数组, 数组], 可选
bin 的规格
如果是整数,表示两个维度(nx=ny=bins)的 bin 数量。
如果是类数组,表示两个维度(x_edges=y_edges=bins)的 bin 边缘。
如果是 [整数, 整数],表示每个维度(nx, ny = bins)的 bin 数量。
如果是 [数组, 数组],表示每个维度(x_edges, y_edges = bins)的 bin 边缘。
可以是 [整数, 数组] 或 [数组, 整数] 的组合,其中整数是 bin 的数量,数组是 bin 边缘。
- range类数组, 形状(2,2), 可选
每个维度 bin 的最左和最右边缘(如果未在 bins 参数中明确指定):
[[xmin, xmax], [ymin, ymax]]。所有在此范围之外的值都将被视为异常值,不计入直方图。- density布尔值, 可选
如果为 False(默认值),返回每个 bin 中的样本数量。如果为 True,返回 bin 处的概率密度函数,即
bin_count / sample_count / bin_area。- weights类数组, 形状(N,), 可选
一个值数组
w_i,用于对每个样本(x_i, y_i)进行加权。如果 density 为 True,权重将归一化为 1。如果 density 为 False,返回的直方图的值等于落入每个 bin 的样本所对应权重的总和。
- 返回:
- Hndarray, 形状(nx, ny)
样本 x 和 y 的二维直方图。 x 中的值沿第一维度进行直方图处理,y 中的值沿第二维度进行直方图处理。
- xedgesndarray, 形状(nx+1,)
沿第一维度的 bin 边缘。
- yedgesndarray, 形状(ny+1,)
沿第二维度的 bin 边缘。
另请参阅
histogram一维直方图
histogramdd多维直方图
注意事项
当 density 为 True 时,返回的直方图是样本密度,其定义为 bin 上的乘积
bin_value * bin_area的总和为 1。请注意,此直方图不遵循笛卡尔约定,即 x 值在横坐标上,y 值在纵坐标上。相反,x 沿数组的第一维度(垂直)进行直方图处理,y 沿数组的第二维度(水平)进行直方图处理。这确保了与
histogramdd的兼容性。示例
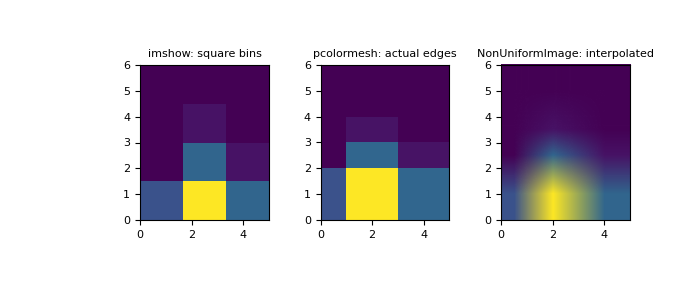
>>> import numpy as np >>> from matplotlib.image import NonUniformImage >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
构建一个具有可变 bin 宽度的二维直方图。首先定义 bin 边缘
>>> xedges = [0, 1, 3, 5] >>> yedges = [0, 2, 3, 4, 6]
接下来我们创建一个包含随机 bin 内容的直方图 H
>>> x = np.random.normal(2, 1, 100) >>> y = np.random.normal(1, 1, 100) >>> H, xedges, yedges = np.histogram2d(x, y, bins=(xedges, yedges)) >>> # Histogram does not follow Cartesian convention (see Notes), >>> # therefore transpose H for visualization purposes. >>> H = H.T
imshow只能显示方形 bin>>> fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 3)) >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(131, title='imshow: square bins') >>> plt.imshow(H, interpolation='nearest', origin='lower', ... extent=[xedges[0], xedges[-1], yedges[0], yedges[-1]]) <matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x...>
pcolormesh可以显示实际边缘>>> ax = fig.add_subplot(132, title='pcolormesh: actual edges', ... aspect='equal') >>> X, Y = np.meshgrid(xedges, yedges) >>> ax.pcolormesh(X, Y, H) <matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x...>
NonUniformImage可用于显示带有插值的实际 bin 边缘>>> ax = fig.add_subplot(133, title='NonUniformImage: interpolated', ... aspect='equal', xlim=xedges[[0, -1]], ylim=yedges[[0, -1]]) >>> im = NonUniformImage(ax, interpolation='bilinear') >>> xcenters = (xedges[:-1] + xedges[1:]) / 2 >>> ycenters = (yedges[:-1] + yedges[1:]) / 2 >>> im.set_data(xcenters, ycenters, H) >>> ax.add_image(im) >>> plt.show()
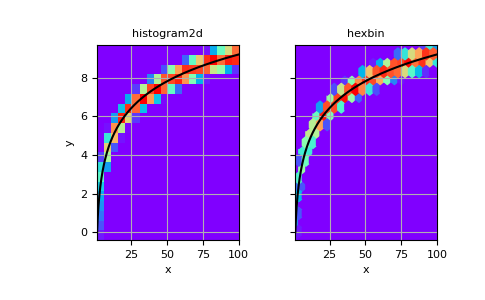
也可以不指定 bin 边缘来构建二维直方图
>>> # Generate non-symmetric test data >>> n = 10000 >>> x = np.linspace(1, 100, n) >>> y = 2*np.log(x) + np.random.rand(n) - 0.5 >>> # Compute 2d histogram. Note the order of x/y and xedges/yedges >>> H, yedges, xedges = np.histogram2d(y, x, bins=20)
现在我们可以使用
pcolormesh绘制直方图,并用hexbin进行比较。>>> # Plot histogram using pcolormesh >>> fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, sharey=True) >>> ax1.pcolormesh(xedges, yedges, H, cmap='rainbow') >>> ax1.plot(x, 2*np.log(x), 'k-') >>> ax1.set_xlim(x.min(), x.max()) >>> ax1.set_ylim(y.min(), y.max()) >>> ax1.set_xlabel('x') >>> ax1.set_ylabel('y') >>> ax1.set_title('histogram2d') >>> ax1.grid()
>>> # Create hexbin plot for comparison >>> ax2.hexbin(x, y, gridsize=20, cmap='rainbow') >>> ax2.plot(x, 2*np.log(x), 'k-') >>> ax2.set_title('hexbin') >>> ax2.set_xlim(x.min(), x.max()) >>> ax2.set_xlabel('x') >>> ax2.grid()
>>> plt.show()